

- #LOCAL DYNAMODB UI ARCHIVE#
- #LOCAL DYNAMODB UI CODE#
- #LOCAL DYNAMODB UI DOWNLOAD#
- #LOCAL DYNAMODB UI FREE#
PS – I almost forgot - check out the DynamoDB mock layers written by AWS customers here. For best results, please head over to the DynamoDB Forum. This post has been very popular and a number of questions have been asked and answered in the comments. You may also find our new Amazon DynamoDB Best Practices, How Tos, and Tools page to be useful.
#LOCAL DYNAMODB UI DOWNLOAD#
Download and unpack the desktop client, change the endpoint inside your app to localhost:8000, and then you can use the desktop client. It starts a server that binds to port 8000 at localhost (or you can specify another port when you start the server). It's a java jar and it runs on Linux and Windows. it is not recommended for production use.ĭownload DynamoDB Local here, give it a shot, and let me know what you think! Documentation can be found here. Amazon provides a local client for DynamoDb.
DynamoDB Local does not have a durability or availability SLA. Your AWS secret key is ignored but must be specified. The values that you supply for the AWS access key and the Region are only used to name the database file. Yes, that's true - you can run your Lambda functions, store data to DynamoDB tables, feed events through Kinesis streams, put your application behind an API Gateway, and much more. In addition, DynamoDB Local does not throttle read or write activity. It spins up a testing environment on your local machine that provides the same functionality and APIs as the real AWS cloud environment. The values that you specify when you call CreateTable and UpdateTable have no effect. DynamoDB Local ignores your provisioned throughput settings. Here are a couple of things to keep in mind as you start to use DynamoDB Local: If you are using the default port, the local endpoint will be localhost:8000. DynamoDB Local listens on port 8000 by default you can change this by specifying the –port option when you start it. Apart from that, I will let you know few issues that you may encounter while adding GSI using CloudFormation and their solutions. Technically my aim for the post is to help you create a DynamoDB table with Global Secondary Index using CloudFormation. The file name will have the form MyAccessKeyId_Region.db, where MyAccessKeyId is the AWS access key used to access DynamoDB Local and Region is the target region.Ĭonfigure your application so that it uses the local endpoint. Well, I wanted to give GSI special attention as there are a lot to talk about them. jar DynamoDBLocal.jarĭynamoDB Local will create a local database in the same directory as the JAR. Note that the Web UI is now deprecated (needs to be activated with STARTWEB1), and requires to use the localstack/localstack-full Docker image. It will not work on older versions of Java.ĭownload the DynamoDB Local JAR, put it in the directory of your choice, and open a command prompt in that directory. PORTWEBUI: Port for the Web user interface / dashboard (default: 8080). 
It will run on Windows, Mac, and Linux systems and is compatible with version 7 of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
#LOCAL DYNAMODB UI ARCHIVE#
No other modifications will be needed.ĭynamoDB Local is available as an executable Java archive (JAR) file. When you are ready to deploy your application, you simply instruct it to connect to the actual DynamoDB endpoint.
#LOCAL DYNAMODB UI CODE#
You can write code while sitting in a tree, on the beach, or in the desert. DynamoDB Local is a client-side database that supports the complete DynamoDB API, but doesn’t manipulate any tables or data in DynamoDB itself. If so, you are going to love our new DynamoDB Local test tool.
#LOCAL DYNAMODB UI FREE#
Lambda.js const services = require('./services.js') Ĭonst dynamoDB = new AWS.DynamoDB(options) Įxports.Would you like to be able to write and test code that uses the Amazon DynamoDB API even if you have no network connection and without incurring any usage charges ( AWS Free Usage Tier notwithstanding)? Invoked lambda.js, but it looks like no result for console.log(err)or console.log(data).Then, I proceed with running AWS SAM sam local start-api -docker-network local-dev.

Until this point, I'm being able to create and list tables using AWS CLI.
Run DynamoDB Local docker run -d -v "$PWD":/dynamodb_local_db -p 8000:8000 -network local-dev -name dynamodb amazon/dynamodb-local. 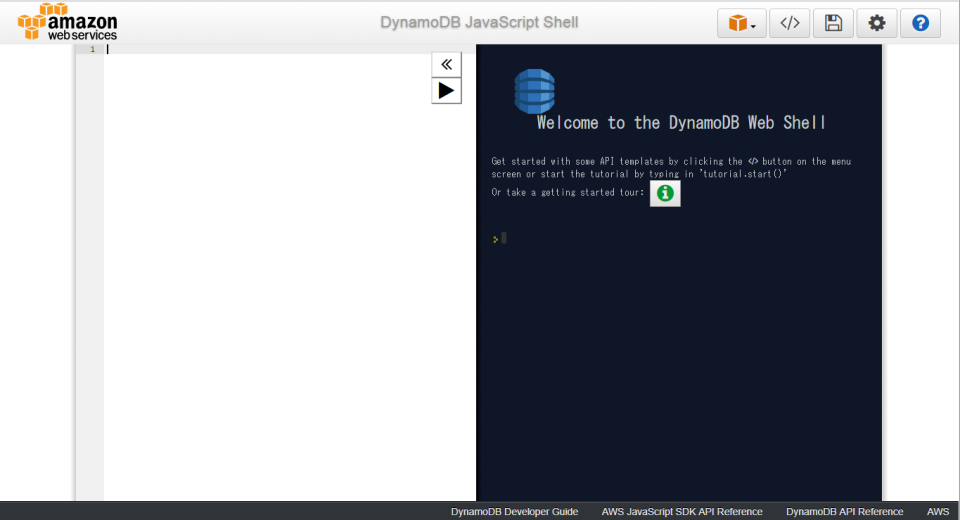 Create new docker network using docker network create local-dev. Here is the steps that I followed (mostly found in the internet) I'm currently testing out AWS SAM with DynamoDB Local using Docker.
Create new docker network using docker network create local-dev. Here is the steps that I followed (mostly found in the internet) I'm currently testing out AWS SAM with DynamoDB Local using Docker.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
